Plugin Information |
|---|
View Android Emulator on the plugin site for more information. |
See also: Android Lint Plugin.
See also: Google Play Android Publisher Plugin.
Features
This plugin lets you automate a number of Android-related tasks during a build:
- Creating a new Android emulator
- Its configuration can be parameterised, including OS version, screen size, locale and hardware properties
- Android SDK dependencies are automatically downloaded and installed
- Running any Android emulator
- Waits until the emulator is fully started-up
- Emulator snapshots can be automatically created
- This allows a very fast startup time for subsequent builds
- This ensures subsequent builds will start from the same clean state
- Logs are automatically captured and saved
- Emulator will be shut down automatically when the build has finished
- Multiple instances of the same emulator are prevented from running concurrently
- Detecting which Android platforms are required to build one or more projects and installing them automatically
- Generating Ant build files for any app, test or library projects found in the workspace
- Installing an Android package onto an emulator
- Uninstalling an Android package from an emulator
- Running the
monkeystress-testing tool - Parsing output from running
monkey- The build outcome can be automatically marked as unstable or failed in case a monkey-induced crash is detected
Requirements
Jenkins
Jenkins version 2.32 or newer is required.
Android
The plugin will automatically download and install the Android SDK, if it's not already installed when a build starts.
This means that no manual effort is required to start running Android emulators with Jenkins.
You can, however, disable automated installation via the "Automatically install Android components when required" option on the main Jenkins configuration page.
Configuration
System configuration
Generally no global configuration is needed — the plugin will try hard to locate an installed Android SDK whenever it is needed. If one is not found, it will be installed automatically.
Job configuration
Running on headless build machines
If you have build slaves which are headless (e.g. Linux servers that don't have a graphical user interface), you can still run an Android Emulator even although, by default, the emulator does require a graphical environment.
Just untick the "Show emulator window" configuration option in your job configuration. This is the equivalent of using the emulator's "-no-window" command-line option.
Other requirements
In addition, while the Android Emulator plugin requires the Port Allocator Plugin, there is no job configuration required for this; everything is handled automatically — you need not select the "Assign unique TCP ports" checkbox in the job config.
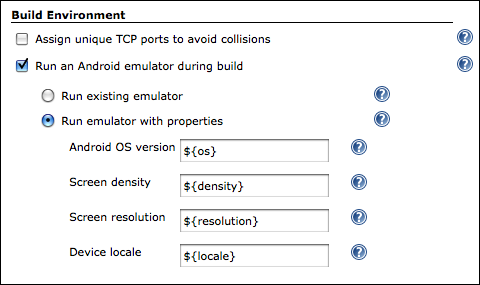
Selecting an emulator
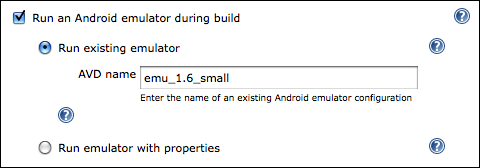
After ticking "Run an Android emulator during build", you will be asked whether you want to run an existing AVD, or whether you want to create a new one on-the-fly with certain properties.
Using an existing emulator for a job just requires that you enter the name of the AVD you want to be started. This AVD must exist on each build node the job will be executed on. Existing AVDs are found in your $HOME/.android/avd directory and can be listed using the "android list avd" command.
As with all other properties, you can enter environment variables here using the format $VARIABLE_NAME.
Alternatively, if you don't have a particular AVD accessible on each build node, the plugin can automatically generate a new emulator if one doesn't already exist:
Each property is mandatory, aside from the device locale. If this is not entered, the Android emulator default locale of US English (en_US) will be used when starting the emulator.
Each field will auto-complete with the default Android SDK values, e.g. 120, 160, 240dpi densities and named screen resolutions including QVGA, HVGA, WVGA etc. However, you can enter your own values if you wish to use a custom OS image, screen density, resolution or locale.
Screen resolutions can be entered either using the named values, or as a "width times height" dimension, e.g. 480x800.
You can specify multiple hardware properties such as the heap size for each Android app, or whether the device has a GPS by clicking the button "Add custom hardware property" and entering the values. See the inline help for more details on the values to enter.
Multi-configuration (matrix) job
The real awesomeness of this plugin comes when used in conjunction with a multi-configuration job type.
By using the "Run emulator with properties" setting, in conjunction with one-or-more matrix axes and the Android Emulator plugin's variable expansion, you can generate and test with a large number of distinct Android emulator configurations with very little effort.
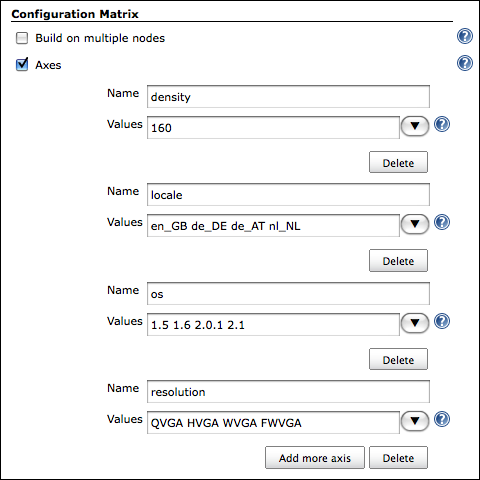
To give a full example, if you want to test your application across multiple Android OS versions, multiple screen densities, multiple screen resolutions and for several target locales, you might set up your matrix axes as follows:
As each of these axis names (i.e. "density", "locale", "os", "resolution") are exported by Jenkins as environment variables, you can make use of these when launching a new Android emulator:
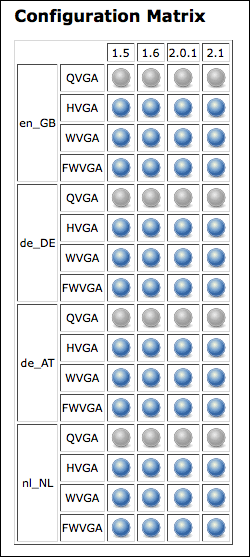
When the build executes, this would automatically generate and allow you to test your application against 64 unique device configurations.
However, you should note that not all combinations are valid. For example, a WVGA (800x480) resolution device makes no sense with a screen density of 120 (unless you have superhuman eyesight).
For this purpose, you can use the "Combination Filter" feature, which tells Jenkins which combinations of the matrix axes are valid. In the case of screen densities and resolutions, a configuration like this should instruct Jenkins to only build for configurations which make sense:
(density=="120").implies(resolution=="QVGA" || resolution=="WQVGA" || resolution=="FWQVGA") && (density=="160").implies(resolution=="HVGA" || resolution=="WVGA" || resolution=="FWVGA") && (density=="240").implies(resolution=="WVGA" || resolution=="FWVGA")
Note that each variable refers to one of the matrix axes, not an Android Emulator plugin property.
Build execution
Environment
For convenience, the plugin places a number of variables into the build environment relating to the emulator in use:
Variable name | Example value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| Identifier for connecting to this AVD, e.g. |
|
| Identifier for connecting to this AVD, e.g. |
|
| Port used by ADB to communicate with the AVD (random for each build) |
|
| Port used to access the AVD's telnet user interface (random for each build) |
|
| Name of the AVD running for the build |
|
| Locale of the AVD |
|
| OS version of the running AVD |
|
| Screen density in dpi of the AVD |
|
| Screen resolution, named or dimension, of the AVD |
|
| Skin being used by the AVD, e.g. |
|
| Port that the AVD server for this build is running on (random for each build) |
|
| Temporary file to which logcat output is written during the build (random for each build) |
|
| The path to the Android SDK being used for this build (optional) |
|
| The path to the Android SDK being used for this build (optional) |
Using the emulator
Now that you have an Android emulator running, you'll probably want to install one or more Android applications (APKs) and start running some tests.
Basically, whenever you want to call adb as part of your build, just call it as you normally would, e.g. adb install my-app.apk.
If you're using Android's default Ant build system, you should specify the sdk.dir property, to tell Ant it can find the Android build scripts:
Just add "sdk.dir=$ANDROID_HOME" to the "Properties" field of your "Invoke Ant" build step.
Installing project prerequisites
When compiling an Android project, you must have all the prerequisite Android platform images installed. For example, if you have an Android app which relies on an Android library project, plus you have a unit test project — these may all be targeting different Android SDK versions, all of which must be present at compile time.
Normally, with the (deprecated) Ant build system, these target versions are specified in either a "project.properties" or "default.properties" file.
Since version 2.1, the plugin provides a "Install Android project prerequisites" build step for the Ant build system, which automatically detects the target versions in the build workspace, then automatically installs any of the corresponding Android platform images that are not yet installed.
This build step requires no configuration — just add it before the build step that compiles your Android projects.
For the Gradle build system, I would recommend including the Android SDK Manager Gradle Plugin in your project. You may have to use JitPack to get the latest version.
Creating project build files
If you only build a project in Eclipse or using another IDE, you may not have the required Ant build files created or checked into your repository.
Since version 2.8, the "Create Android build files" build step will automatically find any Android app, library or test projects in a build's workspace and will create the build files for them, using the appropriate "android update project" command.
Installing and uninstalling APKs
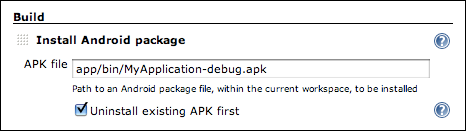
Since version 1.9, the plugin can automatically install an APK on the started emulator for you.
Under the "Build" section of your job configuration, select "Add build step" and choose "Install Android package".
In the "APK file" field that appears, enter the filename of the APK you wish to install. When a build runs, the APK will be automatically installed after the emulator has started up.
Note: It is also possible to use this build step without having started an emulator via this plugin — you can install an APK on an attached device or other emulator.
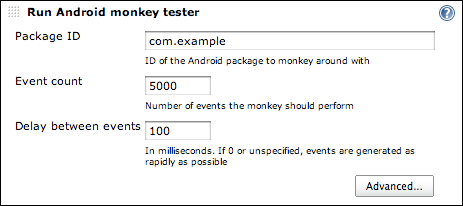
Running the Android monkey tool
The plugin provides a Build Step called "Run Android monkey tester" which will run the monkey stress-testing tool against the given Android package.
The output is saved to a file — by default "monkey.txt" in the root of the build workspace.
Don't forget to archive this file by using "Archive the artifacts" option under "Post-build Actions" if you want to keep the monkey output for future reference!
Parsing monkey output
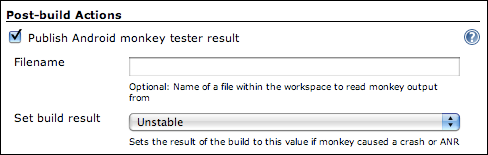
Also provided is a method of parsing the output of the monkey testing tool.
Under the "Post-build Actions" section, enable the "Publish Android monkey tester result". No further configuration is required — by default the plugin will search for "monkey.txt" in the root of the build workspace, parse the file's contents and display the result on the build page.
If the monkey output reveals your Android application crashed or caused an "Application Not Responding" situation, the build will be marked as UNSTABLE.
You can, of course, specify a different filename (including the use of variables) or change the "Set build result" option to mark the build as a FAILURE rather than just UNSTABLE, or leave its status untouched in case the monkey information does not indicate success.
Artifacts
Once the emulator is ready for use, its log is captured until the build finishes. This corresponds to the output of "adb logcat -v time", i.e. the main log output including timestamps.
This will be archived automatically as a build artifact, with the name logcat.txt.
Known issues
Potential upcoming features
- Support for the Pipeline Plugin is planned
- Within the 'android-emulator' component of Jenkins' issue tracker you can:
Version history
Version 3.0 (December 4, 2017)
Many thanks to Michael Musenbrock for doing most of the heavy lifting on this release.
Added support for Android Emulator 2.0 (JENKINS-40178, JENKINS-43215, JENKINS-44490)
The QEMU2 engine will be used automatically, and should be faster and more stable
Older SDK Tools will be automatically upgraded to a modern version as appropriate
Fixed creation of non-default ABI images with SDK Tools < 25.3 (JENKINS-32737)
Thanks to Michael Musenbrock
Fixed to select the configured emulator executable when listing snapshots (JENKINS-34678)
Thanks to Karol Wrótniak
Updated to non-deprecated artifact archiving mechanism (JENKINS-26941)
Thanks to Tarek Belkahia
Added configuration-time check for application ID in the APK uninstall step (PR #53)
Thanks to Sung Kim
Fixed Findbugs warnings, reduced other warnings, and removed deprecated code usages (JENKINS-45456)
Thanks to Michael Musenbrock
Added a Jenkinsfile for ci.jenkins.io
Updated minimum Jenkins version to 2.32
Version 2.15 (May 23, 2016)
- Ensure that newer emulators aren't left running when a build completes (JENKINS-35004)
- This is required as SDK Tools 25.1.6 introduced a breaking change to the emulator console interface
Version 2.14.1 (April 20, 2016)
- Fix crash when using named emulators (JENKINS-34152)
- Updated names and inline help for build steps that create project build files or install prerequisites, to mention that these only work for the deprecated Ant build system
Version 2.14 (April 8, 2016)
- Fixed severe reliability issues when multiple emulators were running at the same time
- Improved emulator startup detection to be more reliable
- Thanks to Andy Piper
- Prevented emulators from using the new QEMU2 engine, which is missing required features (e.g. Android bugs #202762, #202853, #205202, #205204, #205272)
- Ensured that the screen density is configured when creating an emulator
- Added the ability to use the dedicated screen unlock command on Android 6+ (JENKINS-30849)
- Implemented master-agent access control
- When auto-installing the Android SDK, version 24.4.1 is now used
- Added support for newer screen densities that are in use (400, 420, 560dpi)
- Added support for Android 6.0
Version 2.13.1 (April 9, 2015)
- Fixed an issue where the plugin would prematurely declare that an emulator had fully started up (JENKINS-27702)
- Thanks to Mads Kalør
Version 2.13 (March 12, 2015)
- Reverted to the "localhost:XXXX" style of connecting to emulators, as using "emulator-XXXX" seemed to be a very common cause of emulator startup failures (JENKINS-11952)
- Fixed inability to launch Android tools on Unix slaves from a Windows master due to a bad path separator (JENKINS-23134)
- Thanks to Dave Brown
- Fixed the naming of emulators using x86-based Google APIs as Google changed the naming scheme again (JENKINS-23252)
- Fixed the naming of emulators due to a change in the ABI naming format. (JENKINS-25336)
- Thanks to Louis Davin
- Enabled the automated installation of tagged system images, e.g.
android-wear/x86 - Fixed issue where starting a named AVD ignored the configured emulator executable (JENKINS-26338)
- Thanks to Chiara Chiappini
- Fixed the inability to start an emulator in certain cases on 64-bit Mac OS X machines with SDK tools version 23.0.4 or newer (JENKINS-26893)
- Switched to using "init.svc.bootanim" to more reliably detect boot completion, where appropriate (JENKINS-22555)
- Removed reliance on the
aapttool and the unreliable detection code surrounding it - APK install/uninstall build steps now wait for the system package manager to be available before trying to do anything
- Added timeouts to APK install/uninstall build steps as it's not uncommon that
adbhangs during installation (e.g. Android bug #10255) - Added timeouts to
adbwhen attempting to unlock the screen after boot - Increased minimum Jenkins requirement to 1.565.1 to get a crash fix important for Java 8 users (JENKINS-21341)
- Added option to run monkey on multiple (or no) packages or intent categories (JENKINS-13559)
- Thanks to Mads Kalør
- Added option to pass extra command line parameters to the monkey tool (JENKINS-13559)
- The SDK tools and platform tools directories of the SDK in use are now prepended to
$PATHduring a build- This means you no longer need to specify the full path to
adbin an "Execute shell" build step, for example
- This means you no longer need to specify the full path to
- When auto-installing the Android SDK, version 24.0.2 is now used
- Added support for Android 5.1
Version 2.12 (October 21, 2014)
- Added support for Android 5.0, 64-bit system images, and xxxhdpi screen density
- Fix naming of emulator, so that newer x86 images can be used (JENKINS-23252)
- Thanks to Thomas Keller
- Wait for ADB server to start before starting the emulator (JENKINS-11952)
- Should help with cases where the emulator starts faster than the ADB server
- Thanks to Richard Mortimer
Version 2.11.1 (May 19, 2014)
- Added support for Android 4.3 and 4.4
Version 2.11 (May 18, 2014)
- Fixed problem connecting to ADB with non four-digit port numbers (JENKINS-12821, JENKINS-20819)
- This should enable connecting to emulators from the android-maven-plugin
- Thanks to Richard Mortimer
- Use "emulator" instead of "localhost" when connecting to emulators (JENKINS-12821, JENKINS-22334)
- This should fix strange connection failures or multiple devices which started appearing in recent SDK tools versions
- Thanks to Richard Mortimer
- Added support for build-tools so that aapt can be located in newer SDKs (JENKINS-18584)
- Thanks to Steve Moyer
- Work around Android bug #34233 when parsing the snapshot list
- Thanks to Matt McClure
- Fixed parsing of snapshot list, for snapshots larger than 1GB
- Thanks to Matt McClure
- Fixed automated opt-out of usage statistics (JENKINS-14557, JENKINS-21280)
- Thanks to Matt McClure
- Increased emulator startup timeout from 180 to 360 seconds
- Thanks to Matt McClure
- Fixed parsing of relative paths on Windows (JENKINS-18970).
- Thanks to Aitor Mendaza-Ormaza
- Accept multi-line properties when parsing project.properties files (JENKINS-22530)
- Thanks to xstex
- Allow adding a suffix to generated AVD names (JENKINS-11083)
- This makes it possible to use the exact same emulator config in two jobs without one job having to block waiting for the other job to finish using the emulator.
- Thanks to Hasan Hosgel and Payman Delshad
- Fixed paths to ensure the inline help text should always be properly displayed (JENKINS-20303)
- Ensure that system images are installed in all cases where required (JENKINS-17532)
- Ensure that named AVDs still work, even when "keep AVDs in workspace" is enabled (JENKINS-18919)
- Ensure the "Create project files" build step always imports or installs an Android SDK
- Emulator window is no longer shown by default
- Emulator snapshots are no longer enabled by default as they are not very reliable (JENKINS-17126)
- Don't allow multiple jobs to block each other, if they use build parameters to set emulator properties
- Removed incorrect warnings about potentially incorrect density/resolution configuration (JENKINS-13313)
- When auto-installing the Android SDK, version 22.6.2 is now used
- Explicitly added MIT licence to the project config (JENKINS-20009)
Version 2.10 (June 3, 2013)
- Fixed problems with Android 2.3.3 emulators caused by renaming the x86 ABI package (JENKINS-14741)
- Licence agreements are accepted when auto-installing SDK components (JENKINS-17997)
- Fixed auto-detection of the SDK in PATH (JENKINS-17816)
- Updated SDK auto-detection to handle the new 'build-tools' SDK component (JENKINS-18015)
- Various new components are now automatically installed along with the SDK
- Build Tools
- Android and Google local m2 repositories for use with Gradle builds
- When auto-installing the Android SDK, version 21.0.1 is now used
Version 2.9.1 (April 12, 2013)
- Fixed a regression in 2.9 which could cause problems running
adbfrom certain build steps
Version 2.9 (April 11, 2013)
- Improved detection of app project when creating build files for a test project (JENKINS-17531)
- ABI field is now ignored when creating emulators which don't support ABIs (JENKINS-14741)
- Resolved issue when automatically installing SDK on a slave (JENKINS-16720)
- Builds can now be failed if package installation fails (JENKINS-13932)
- Builds can now be failed if package uninstallation fails (JENKINS-16246)
- SD card value in matrix jobs is no longer altered when saving configuration (JENKINS-13931)
- Set LD_LIBRARY_PATH for emulator to run on 64-bit Linux (JENKINS-14901)
- Added environment variable pointing to temporary logcat file during a build (JENKINS-12572)
- Added documentation for 'Create Android build files' step (JENKINS-17456)
- Raised required Jenkins version to 1.466; Hudson is no longer supported
Version 2.8.1 (February 11, 2013)
- Fix issues with "Create Android build files" build step when running on slaves, or on projects in the workspace root
- Updated all links to android.com in the inline help, since Android moved some pages without redirecting the URL (see JENKINS-14860)
Version 2.8 (February 1, 2013)
- Add build step which creates Android build files for app, library and test projects
- When auto-installing the Android SDK, now a more up-to-date version is installed (20.0.1)